人工智能
一、人工智能概述
- 快速的AI发展
AI正在以惊人的速度改变世界,从艺术创作到商业应用,再到编程开发,AI 的影响力无处不在。这是最近两年AI发展的几个案例:
- Midjourney: 这个由仅 11 人团队开发的 AI 图像生成工具,凭借其强大的图像生成能力,迅速吸引了大量用户,并实现了营收过亿美元的惊人成绩。
- ChatGPT: OpenAI 推出的 ChatGPT 在短短几个月内月活跃用户数突破 5.64 亿,其母公司OpenAI估值也超过了 1600 亿美元,成为 AI 领域的明星企业。
- NVIDIA: 作为 AI 计算领域的领导者,NVIDIA 的市值因 AI 的蓬勃发展而突破 3 万亿美元,其 GPU 产品成为训练和运行 AI 模型的基石。
在编程领域,AI 工具也正在帮助开发者大幅提升效率,最近在社交媒体也都已经刮起了“我不会编程,但是我会AI编程”:
- Cursor: 这款 AI 代码编辑器可以理解代码上下文,提供智能生成代码、智能代码补全、错误检测和修复建议,帮助开发者更快地编写高质量的代码。
- GitHub Copilot: 作为 GitHub 推出的 AI 编程助手,Copilot 可以根据代码注释和上下文自动生成代码片段,甚至完成整个函数,极大地提高了开发效率。
- 通义灵码: 阿里巴巴推出的 AI 编程助手,支持多种编程语言,提供代码补全、代码优化、代码解释等功能,帮助开发者更高效地完成开发任务。
-
机器学习与深度学习
- 机器学习 是人工智能的核心方法,旨在通过数据训练模型,使计算机能够从数据中学习规律并做出预测或决策。机器学习分为监督学习、无监督学习和强化学习。
- 深度学习 是机器学习的一个子领域,通过构建多层的神经网络模型来学习数据的特征表示。深度学习在图像识别、自然语言处理等领域取得了突破性进展。
- 强化学习 是一种通过与环境交互来学习最优策略的机器学习方法。它通过试错和奖励机制来优化决策,广泛应用于游戏 AI、机器人控制等领域。
简单来说,深度学习是机器学习的一种实现方式,而强化学习是机器学习的一个分支。

-
深度学习模型架构与应用
-
卷积神经网络 (CNN)
CNN 是一种专门用于处理图像数据的神经网络。它的核心思想是通过卷积操作提取图像的局部特征,再通过池化操作降低数据维度。
-
循环神经网络 (RNN)
RNN 是一种用于处理序列数据的神经网络。它的特点是能够记住之前的状态,并将这些信息用于当前的计算。
-
长短期记忆网络 (LSTM)
LSTM 是 RNN 的改进版本,解决了 RNN 在处理长序列数据时容易遗忘的问题。它通过引入“记忆单元”来更好地保存长期信息
-
注意力机制 (Attention)
注意力机制是一种让模型能够专注于输入数据中重要部分的技术。它通过计算权重来决定哪些部分需要更多关注。
-
Transformer 模型
Transformer 是一种基于注意力机制的模型,彻底改变了自然语言处理领域。它通过自注意力机制捕捉输入数据之间的关系,避免了 RNN 的序列计算问题。
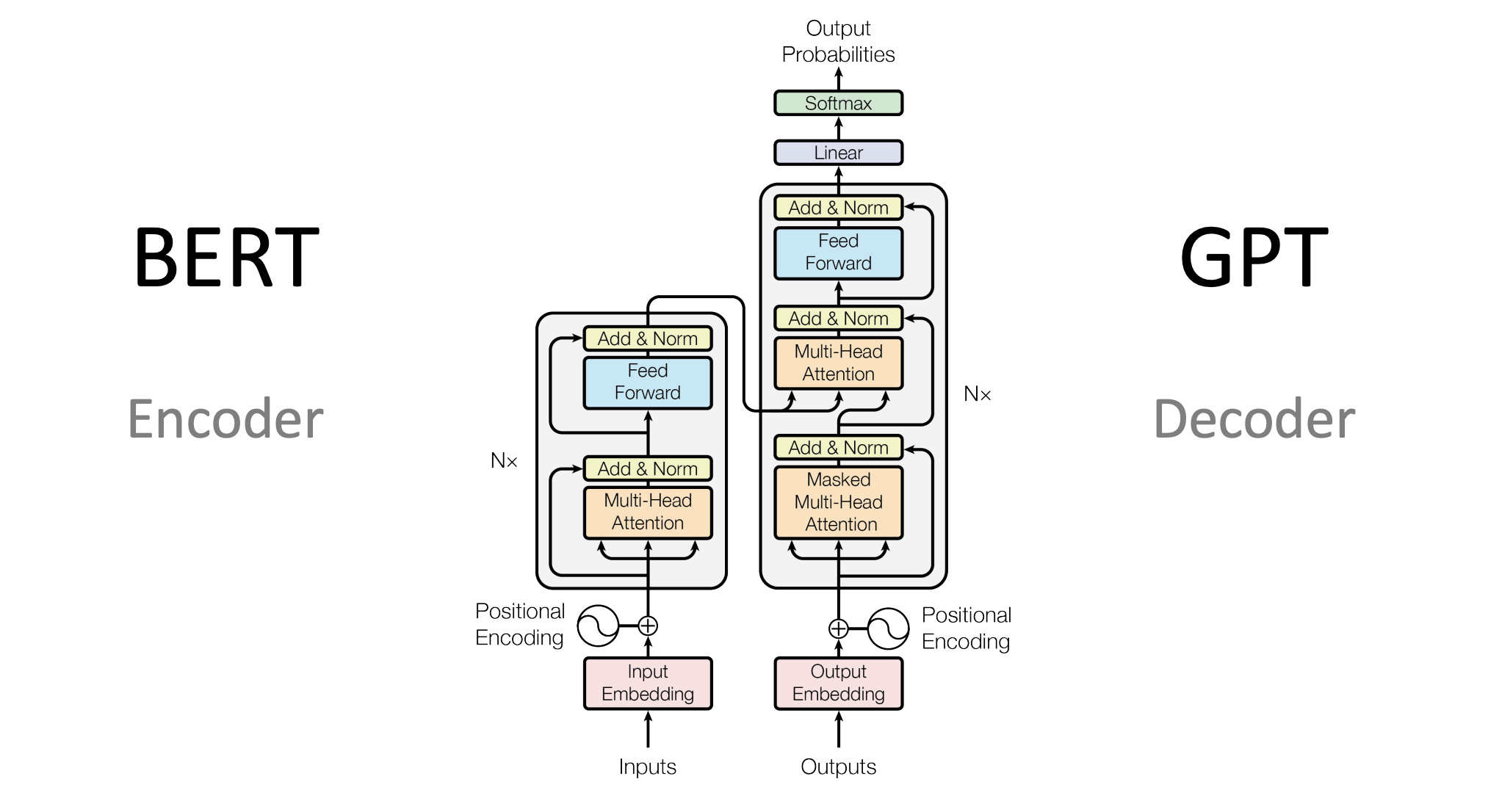
-
三、基于 LLM 的开发
1. 大型语言模型 (LLM) 简介
大型语言模型(Large Language Model, LLM)是近年来人工智能领域最重要的突破之一。它们通过海量文本数据的训练,能够理解和生成自然语言,并在各种任务中表现出色。
- 概念:LLM 是一种基于深度学习的模型,通常使用 Transformer 架构,通过预训练和微调的方式学习语言的统计规律和语义信息。
- 发展历程:
- 早期语言模型(如 n-gram)只能处理简单的文本任务。
- 随着深度学习的发展,RNN 和 LSTM 被用于语言建模,但受限于计算能力和数据规模。
- Transformer 模型的提出(如 GPT、BERT)彻底改变了自然语言处理领域,LLM 开始展现出强大的能力。
- 近年来,随着计算资源的提升和数据规模的扩大,LLM 的规模不断增长(如 GPT-3、GPT-4),能力也越来越强。
- 应用场景:
- 文本生成:如写作助手、代码生成、创意文案等。
- 问答系统:如智能客服、知识问答等。
- 机器翻译:如跨语言文本翻译。
- 文本摘要:如从长篇文章中提取关键信息。
- 演示:使用 OpenAI API 调用 GPT 模型:
- 介绍 OpenAI API 的基本使用方法。
- 示例代码:调用 GPT 模型生成文本。
from openai import OpenAI client = OpenAI(base_url=r"http://180.153.21.76:17009/v1", api_key="111") response = client.chat.completions.create( model = "Qwen-72B", messages=[ {"role": "user", "content": "写一段关于人工智能的简短介绍:"} ] ) print(response.choices[0].message.content)
2. 检索增强生成 (RAG)
检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation, RAG)是一种结合检索和生成的技术,通过从外部知识库中检索相关信息来增强语言模型的生成能力。
-
原理:
- RAG 模型由两部分组成:检索器和生成器。
- 检索器从外部知识库中检索与输入相关的文档或信息。
- 生成器(通常是 LLM)根据检索到的信息和输入生成最终的输出。
-
优势:
- 解决 LLM 的“知识截止”问题:通过检索外部知识,RAG 可以生成更准确、更实时的内容。
- 提高生成内容的可信度:基于真实数据生成的结果更具说服力。
- 改善模型幻觉,减少模型输出虚假错误信息。
-
代码演示:使用 LangChain 实现一个简单的 RAG 应用:
- 安装 LangChain 和 OpenAI:
pip install langchain openai - 示例代码:使用 LangChain 实现 RAG:
from langchain_text_splitters import CharacterTextSplitter from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings from langchain_community.document_loaders import Docx2txtLoader from langchain_chroma import Chroma from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI # 加载文档 loader = Docx2txtLoader("人工智能.docx") data = loader.load() # 内容切割 text_splitter = CharacterTextSplitter( separator="\n\n", chunk_size=100, chunk_overlap=20, length_function=len, is_separator_regex=False,
)
texts = text_splitter.split_documents(data)
创建向量数据库
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(api_key="xxx", base_url="http://180.153.21.76:12118/v1", model="ODB", ) db = Chroma(client=persistent_client, collection_name="xxx", embedding_function=embeddings)
创建检索器
retriever = db.as_retriever()
创建 LLM
llm = ChatOpenAI(base_url=r"http://104.215.28.223:8080/v1", api_key="111", model="Qwen2.5-72B")
创建 RAG 链
qa_chain = RetrievalQA.from_chain_type(llm=llm, chain_type="stuff", retriever=retriever)
提问并获取答案
query = "什么是人工智能?" result = qa_chain.run(query) print(result)
- 安装 LangChain 和 OpenAI:
更多
从基础的 RAG 到其进阶版本如 GraphRAG 和 Advanced RAG,再到引入混合检索和 Reranker 的优化,检索增强生成(Retrieval-Augmented Generation)技术不断演进。通过对检索模块的精细化设计,如多跳检索、密集检索、图结构建模等,RAG 框架在特定任务上的表现往往能够超越更高参数量的纯生成模型。这种优化不仅提升了生成质量,还显著降低了计算成本。更重要的是,在开发工程中,检索增强的优化空间巨大,开发者可以通过调整检索策略、优化索引结构、引入领域知识等方式,进一步提升系统性能,展现了检索增强生成在知识密集型任务中的强大潜力与工程灵活性。
四、AI Agent 的应用与发展
1. AI Agent 简介
AI Agent(人工智能代理)是一种能够感知环境、做出决策并执行任务的智能系统。它结合了感知、推理、学习和行动能力,旨在模拟人类或生物的智能行为。
- 概念:AI Agent 是一个自主运行的实体,能够通过传感器感知环境,通过算法做出决策,并通过执行器与环境交互。
- 分类:
- 基于规则的系统:通过预定义的规则执行任务,适用于简单、明确的任务。
- 基于学习的系统:通过机器学习或强化学习从数据中学习策略,适用于复杂、动态的环境。
- 混合系统:结合规则和学习的优势,适用于需要灵活性和可靠性的任务。
- 应用场景:
- 智能助手:如 Siri、Alexa,帮助用户完成日常任务。
- 自动驾驶:通过感知和决策系统实现车辆的自主驾驶。
- 游戏 AI:如 AlphaGo,在复杂游戏中击败人类选手。
- 工业自动化:如机器人,在工厂中执行重复性任务。
2. AutoGPT 和 BabyAGI
AutoGPT 和 BabyAGI 是两种基于大型语言模型(LLM)的 AI Agent,它们能够自主完成任务并表现出一定的推理和规划能力。
- AutoGPT:
- 简介:AutoGPT 是一个开源项目,基于 GPT 模型,能够自主分解任务、制定计划并执行。
- 使用方法:
- 安装 AutoGPT 并配置 API 密钥。
- 设置任务目标,例如“研究 AI 的最新发展趋势并生成报告”。
- AutoGPT 会自动分解任务、搜索信息、生成内容并保存结果。
- 优点:
- 自主性强,能够处理复杂任务。
- 可扩展性高,支持多种插件和工具。
- 缺点:
- 运行成本较高,需要频繁调用模型与接口。
- 任务执行过程中可能出现偏差或错误。
- 应用场景:市场调研、内容生成、自动化办公等。
- 运行案例:
import { AutoGPT } from "langchain/experimental/autogpt"; import { ReadFileTool, WriteFileTool } from "langchain/tools"; import { InMemoryFileStore } from "langchain/stores/file/in_memory"; import { MemoryVectorStore } from "langchain/vectorstores/memory"; import { OpenAIEmbeddings, ChatOpenAI } from "@langchain/openai"; import { SerpAPI } from "@langchain/community/tools/serpapi"; const store = new InMemoryFileStore(); const tools = [ new ReadFileTool({ store }), new WriteFileTool({ store }), new SerpAPI(process.env.SERPAPI_API_KEY, { location: "San Francisco,California,United States", hl: "en", gl: "us", }), ]; const vectorStore = new MemoryVectorStore(new OpenAIEmbeddings()); const autogpt = AutoGPT.fromLLMAndTools( new ChatOpenAI({ temperature: 0 }), tools, { memory: vectorStore.asRetriever(), aiName: "Tom", aiRole: "Assistant", } ); await autogpt.run(["write a weather report for SF today"]); /* { "thoughts": { "text": "I need to write a weather report for SF today. I should use a search engine to find the current weather conditions.", "reasoning": "I don't have the current weather information for SF in my short term memory, so I need to use a search engine to find it.", "plan": "- Use the search command to find the current weather conditions for SF\n- Write a weather report based on the information found", "criticism": "I need to make sure that the information I find is accurate and up-to-date.", "speak": "I will use the search command to find the current weather conditions for SF." }, "command": { "name": "search", "args": { "input": "current weather conditions San Francisco" } } } { "thoughts": { "text": "I have found the current weather conditions for SF. I need to write a weather report based on this information.", "reasoning": "I have the information I need to write a weather report, so I should use the write_file command to save it to a file.", "plan": "- Use the write_file command to save the weather report to a file", "criticism": "I need to make sure that the weather report is clear and concise.", "speak": "I will use the write_file command to save the weather report to a file." }, "command": { "name": "write_file", "args": { "file_path": "weather_report.txt", "text": "San Francisco Weather Report:\n\nMorning: 53°, Chance of Rain 1%\nAfternoon: 59°, Chance of Rain 0%\nEvening: 52°, Chance of Rain 3%\nOvernight: 48°, Chance of Rain 2%" } } } { "thoughts": { "text": "I have completed all my objectives. I will use the finish command to signal that I am done.", "reasoning": "I have completed the task of writing a weather report for SF today, so I don't need to do anything else.", "plan": "- Use the finish command to signal that I am done", "criticism": "I need to make sure that I have completed all my objectives before using the finish command.", "speak": "I will use the finish command to signal that I am done." }, "command": { "name": "finish", "args": { "response": "I have completed all my objectives." } } } */
- BabyAGI:
- 简介:BabyAGI 是一个轻量级的任务驱动型 AI Agent,能够根据目标生成任务列表并逐步完成。
- 使用方法:
- 配置 BabyAGI 的环境和 API 密钥。
- 设置初始任务,例如“制定一个学习 AI 的计划”。
- BabyAGI 会自动生成子任务并执行,例如“搜索 AI 学习资源”、“制定学习时间表”等。
- 优点:
- 结构简单,易于理解和定制。
- 任务分解能力强,适合多步骤任务。
- 缺点:
- 开发工程繁琐,需要更多的算法兜底。
- 需要较低工具接口提供辅助。
- 应用场景:任务管理、学习规划、项目管理等。
3. AI Agent 的未来发展
AI Agent 正在快速发展,未来可能会在以下方面取得突破:
-
多模态交互:
- AI Agent 将能够处理多种类型的数据(如文本、图像、语音),并实现更自然的交互。
- 例如,一个 AI Agent 可以通过语音指令控制智能家居设备,同时分析摄像头画面来调整环境。
-
自主学习:
- AI Agent 将具备更强的自主学习能力,能够从环境中不断学习并优化策略。
- 例如,一个 AI Agent 可以通过试错学习如何在复杂环境中完成特定任务。
-
协作与通信:
- 多个 AI Agent 将能够协作完成任务,并通过通信共享信息和资源。
- 例如,在自动驾驶中,多辆车可以通过 AI Agent 协同规划路线,避免拥堵。
-
挑战与伦理问题:
- 技术挑战:如何提高 AI Agent 的可靠性、安全性和可解释性。
- 伦理问题:如何确保 AI Agent 的行为符合道德规范,避免滥用或误用。
- 社会影响:AI Agent 的普及可能对就业、隐私和社会结构产生深远影响。
五、 大模型的部署
huggingface 的模型部署
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer model_name = "Qwen/Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct" model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained( model_name, torch_dtype="auto", device_map="auto" ) tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name) prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language model." messages = [ {"role": "system", "content": "You are Qwen, created by Alibaba Cloud. You are a helpful assistant."}, {"role": "user", "content": prompt} ] text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template( messages, tokenize=False, add_generation_prompt=True ) model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device) generated_ids = model.generate( **model_inputs, max_new_tokens=512 ) generated_ids = [ output_ids[len(input_ids):] for input_ids, output_ids in zip(model_inputs.input_ids, generated_ids) ] response = tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)[0]
Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct模型config.json配置
{ "architectures": [ "Qwen2ForCausalLM" // 模型架构,用于因果语言建模 ], "attention_dropout": 0.0, // 注意力机制中的dropout率,0.0表示不使用dropout "bos_token_id": 151643, // 开始符(Beginning of Sequence)的token ID "eos_token_id": 151645, // 结束符(End of Sequence)的token ID "hidden_act": "silu", // 隐藏层激活函数,这里使用SILU(Swish)激活函数 "hidden_size": 8192, // 隐藏层的大小,即每个隐藏层的神经元数量 "initializer_range": 0.02, // 参数初始化的范围 "intermediate_size": 29568, // 中间层的大小,通常用于Transformer中的前馈网络 "max_position_embeddings": 32768, // 最大位置编码的长度,即模型能处理的最大序列长度 "max_window_layers": 70, // 最大窗口层数,可能用于滑动窗口注意力机制 "model_type": "qwen2", // 模型类型,标识为qwen2 "num_attention_heads": 64, // 注意力头的数量 "num_hidden_layers": 80, // 隐藏层的数量 "num_key_value_heads": 8, // 键值头的数量,用于多头注意力机制 "rms_norm_eps": 1e-06, // RMS归一化中的epsilon值,用于数值稳定性 "rope_theta": 1000000.0, // RoPE(Rotary Position Embedding)的theta参数 "sliding_window": 131072, // 滑动窗口的大小,可能用于限制注意力机制的范围 "tie_word_embeddings": false, // 是否绑定输入和输出的词嵌入,false表示不绑定 "torch_dtype": "bfloat16", // PyTorch数据类型,这里使用bfloat16 "transformers_version": "4.43.1", // 使用的transformers库版本 "use_cache": true, // 是否使用缓存,true表示使用 "use_sliding_window": false, // 是否使用滑动窗口注意力机制,false表示不使用 "vocab_size": 152064 // 词汇表的类型数量,模型的词汇表中有 152,064 个不同的 token(可能是单词、子词或字符等) }
Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct模型generation_config.json配置
{ "bos_token_id": 151643, // 开始符(Beginning of Sequence)的token ID "pad_token_id": 151643, // 填充符(Padding)的token ID,用于填充序列到相同长度 "do_sample": true, // 是否使用采样生成文本,true表示使用采样策略而非贪婪解码 "eos_token_id": [ // 结束符(End of Sequence)的token ID,可以是单个值或列表 151645, // 第一个结束符的token ID 151643 // 第二个结束符的token ID ], "repetition_penalty": 1.05, // 重复惩罚系数,用于降低生成重复文本的概率,值大于1.0会减少重复 "temperature": 0.7, // 温度参数,控制生成文本的随机性,值越低生成结果越确定,值越高越随机 "top_p": 0.8, // Top-p(核采样)参数,仅从累积概率超过p的最小token集合中采样 "top_k": 20, // Top-k参数,仅从概率最高的k个token中采样 "transformers_version": "4.37.0" // 使用的transformers库版本 }
Qwen2.5-72B-Instruct模型tokenizer_config.json配置
{ "add_bos_token": false, // 是否在输入序列前添加开始符(Beginning of Sequence),false表示不添加 "add_prefix_space": false, // 是否在输入文本前添加空格,false表示不添加 "added_tokens_decoder": { // 解码器中添加的特殊token及其属性 "151643": { "content": "<|endoftext|>", // token内容 "lstrip": false, // 是否在左侧去除空格,false表示不去除 "normalized": false, // 是否进行归一化处理,false表示不处理 "rstrip": false, // 是否在右侧去除空格,false表示不去除 "single_word": false, // 是否作为单个单词处理,false表示不作为单个单词 "special": true // 是否为特殊token,true表示是 }, "151644": { "content": "<|im_start|>", "lstrip": false, "normalized": false, "rstrip": false, "single_word": false, "special": true }, "151645": { "content": "<|im_end|>", "lstrip": false, "normalized": false, "rstrip": false, "single_word": false, "special": true }, ...... }, "additional_special_tokens": [ // 额外的特殊token列表 "<|im_start|>", "<|im_end|>", "<|object_ref_start|>", "<|object_ref_end|>", "<|box_start|>", "<|box_end|>", "<|quad_start|>", "<|quad_end|>", "<|vision_start|>", "<|vision_end|>", "<|vision_pad|>", "<|image_pad|>", "<|video_pad|>" ], "bos_token": null, // 开始符(Beginning of Sequence),null表示未设置 "chat_template": "{%- if tools %}\n {{- '<|im_start|>system\\n' }}\n {%- if messages[0]['role'] == 'system' %}\n {{- messages[0]['content'] }}\n {%- else %}\n {{- 'You are Qwen, created by Alibaba Cloud. You are a helpful assistant.' }}\n {%- endif %}\n {{- \"\\n\\n# Tools\\n\\nYou may call one or more functions to assist with the user query.\\n\\nYou are provided with function signatures within <tools></tools> XML tags:\\n<tools>\" }}\n {%- for tool in tools %}\n {{- \"\\n\" }}\n {{- tool | tojson }}\n {%- endfor %}\n {{- \"\\n</tools>\\n\\nFor each function call, return a json object with function name and arguments within <tool_call></tool_call> XML tags:\\n<tool_call>\\n{\\\"name\\\": <function-name>, \\\"arguments\\\": <args-json-object>}\\n</tool_call><|im_end|>\\n\" }}\n{%- else %}\n {%- if messages[0]['role'] == 'system' %}\n {{- '<|im_start|>system\\n' + messages[0]['content'] + '<|im_end|>\\n' }}\n {%- else %}\n {{- '<|im_start|>system\\nYou are Qwen, created by Alibaba Cloud. You are a helpful assistant.<|im_end|>\\n' }}\n {%- endif %}\n{%- endif %}\n{%- for message in messages %}\n {%- if (message.role == \"user\") or (message.role == \"system\" and not loop.first) or (message.role == \"assistant\" and not message.tool_calls) %}\n {{- '<|im_start|>' + message.role + '\\n' + message.content + '<|im_end|>' + '\\n' }}\n {%- elif message.role == \"assistant\" %}\n {{- '<|im_start|>' + message.role }}\n {%- if message.content %}\n {{- '\\n' + message.content }}\n {%- endif %}\n {%- for tool_call in message.tool_calls %}\n {%- if tool_call.function is defined %}\n {%- set tool_call = tool_call.function %}\n {%- endif %}\n {{- '\\n<tool_call>\\n{\"name\": \"' }}\n {{- tool_call.name }}\n {{- '\", \"arguments\": ' }}\n {{- tool_call.arguments | tojson }}\n {{- '}\\n</tool_call>' }}\n {%- endfor %}\n {{- '<|im_end|>\\n' }}\n {%- elif message.role == \"tool\" %}\n {%- if (loop.index0 == 0) or (messages[loop.index0 - 1].role != \"tool\") %}\n {{- '<|im_start|>user' }}\n {%- endif %}\n {{- '\\n<tool_response>\\n' }}\n {{- message.content }}\n {{- '\\n</tool_response>' }}\n {%- if loop.last or (messages[loop.index0 + 1].role != \"tool\") %}\n {{- '<|im_end|>\\n' }}\n {%- endif %}\n {%- endif %}\n{%- endfor %}\n{%- if add_generation_prompt %}\n {{- '<|im_start|>assistant\\n' }}\n{%- endif %}\n", // Jinja2 的聊天模板,用于生成对话格式 "clean_up_tokenization_spaces": false, // 是否清理tokenization后的空格,false表示不清理 "eos_token": "<|im_end|>", // 结束符(End of Sequence) "errors": "replace", // 处理错误的方式,replace表示用替换字符处理 "model_max_length": 131072, // 模型支持的最大输入长度 "pad_token": "<|endoftext|>", // 填充符(Padding) "split_special_tokens": false, // 是否拆分特殊token,false表示不拆分 "tokenizer_class": "Qwen2Tokenizer", // tokenizer的类名 "unk_token": null // 未知token,null表示未设置 }
GPU硬件层面参数
HF Transformers : model_name_or_path: 模型路径 device_map: 设备映射 torch_dtype: 数据类型 max_memory: 最大内存
基于VLLM推理加速部署: model:模型路径 tokenizer:tokenizer路径 device:设备 trust-remote-code:是否信任远程代码 dtype:数据类型 kv-cache-dtype:键值缓存数据类型(fp8, fp8_e5m2, fp8_e4m3) pipeline-parallel-size:管道并行大小 tensor-parallel-size:张量并行大小 gpu-memory-utilization:GPU内存利用率